
How process optimization helps you move to the next level?
What is the optimal set of processes to allocate our resources? What process and steps do we have? These questions seem like questions that every company should answer easily. Unfortunately, a lot of companies are not able to do so. Their processes are just too complex because of changing price constraints, or other variables. There is a solution: Process optimization.
What is process optimization?
In theory, the concept of process optimization is relatively simple. A process is optimized based on a certain measurement and given a set of constraints and variables. Examples of measurements are profit, production, and costs which are maximized or minimized. Typical constraints are production capacity, demand- and supply of goods. Prices and costs are examples of variables that change and have an effect on the outcome. A process that can be optimized is characterized by different process steps where a choice can be made. Eventually, this choice affects the total outcome.
The process
Generally, a process has a large set of constraints. It’s a list of variables that change over time and a set of different inputs that make use of the same capacity in different locations. As a result, the optimal allocation also differs over time and is rarely easily calculated. This is where process optimization comes in handy. A linear optimization model calculates the optimal allocation of resources.
Flexibility
This model is flexible and calculates a new optimal allocation if one of the variables or constraints changes. Because of this flexibility, a business user can answer questions such as: What are the optimal allocations of different products? What is the effect of a change in the price, demand, or supply? Faster and based on (new) data instead of based on gut feeling. See the example below.
Relevant industries/companies
Overall, process optimization is relevant for all companies where their (production) process is characterized by the characteristics from above. Process optimization is, for instance, relevant for an operational manager of a production company with a hundred different products that are produced in different locations. And sell to a different buyer for market prices who want to optimize its profit. But also for a smaller company that is looking for the optimal machine setting to minimize the costs.
Process optimization example
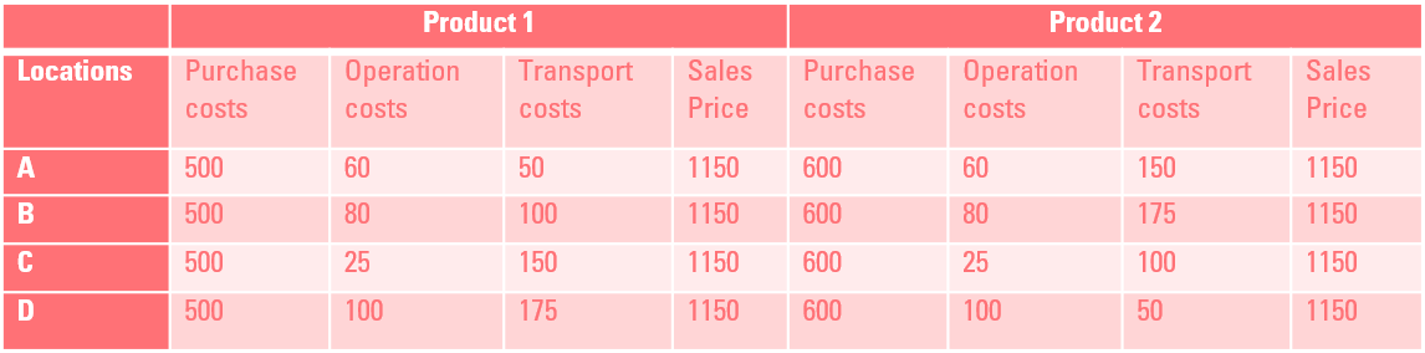
In this example, we as data scientist got a question from an operational director to optimize the production process. In this case, product 1 (Quantity = 1000) & product 2 (Quantity = 750) takes place in four locations; each location has a capacity of 500 units. Other variables such as the costs and the prices depend on the product and the location of production, see table below:
Combination Power BI and Python
Particularly, this linear optimization task is performed with the Scipy library in Python. The outcomes are visualized in Power BI. The Python code runs in the background. This Power BI dashboard provides an overview of the optimal allocation, the results can also be incorporated in other dashboards and/or reports. Power BI provides the opportunity to share the outcomes with colleagues.
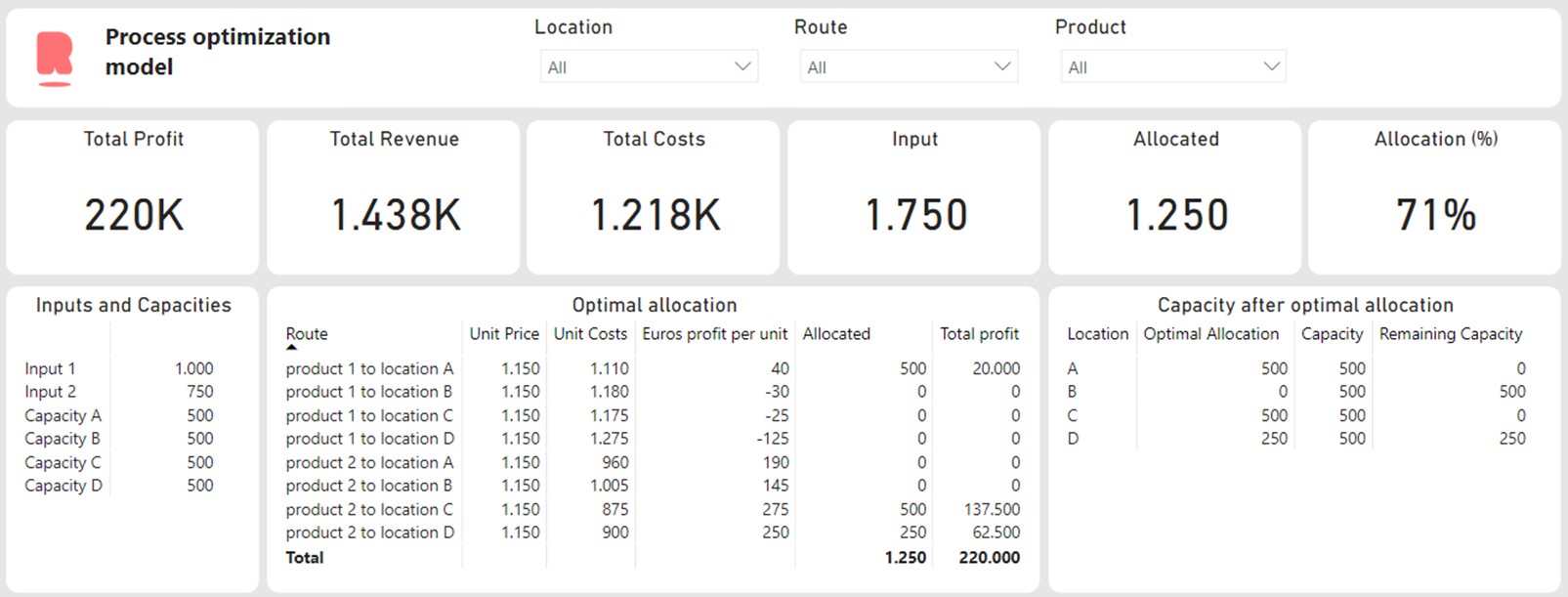
Example Python Code
For example, in this dashboard, the Python code is integrated into the Power BI dashboard. This gives us the ability to include Power BI parameters in the Python code, which we can modify. A big advantage is that the model is flexible, and a user can test some scenarios or change variables if needed without adjusting the Python code. Let’s say we want to know what a sales price increase of 50 euros in location B for product 1 will do to our profit and production. Then we can easily do so by changing the parameters. See gif below:
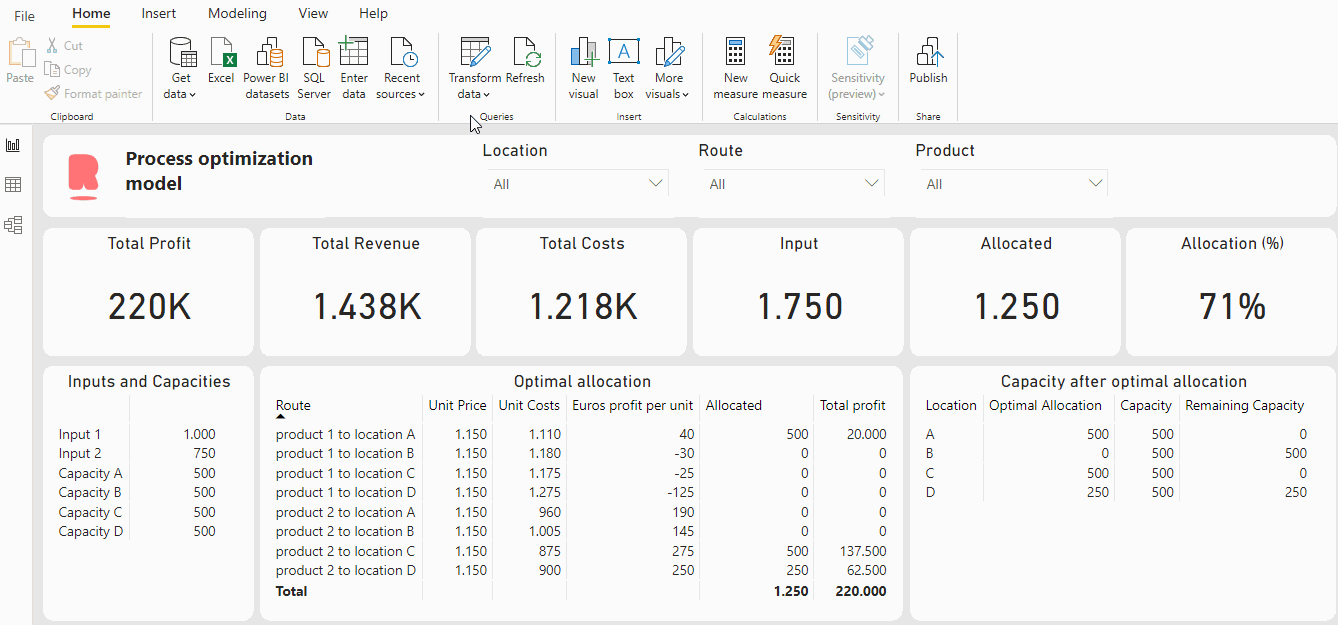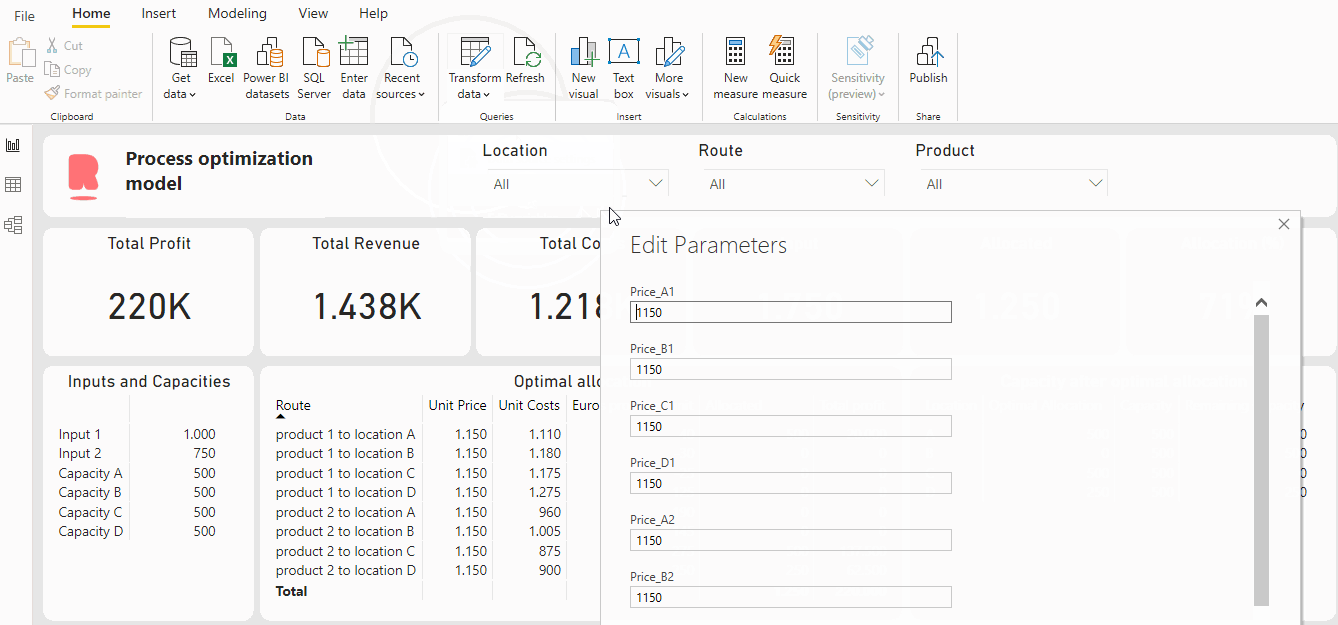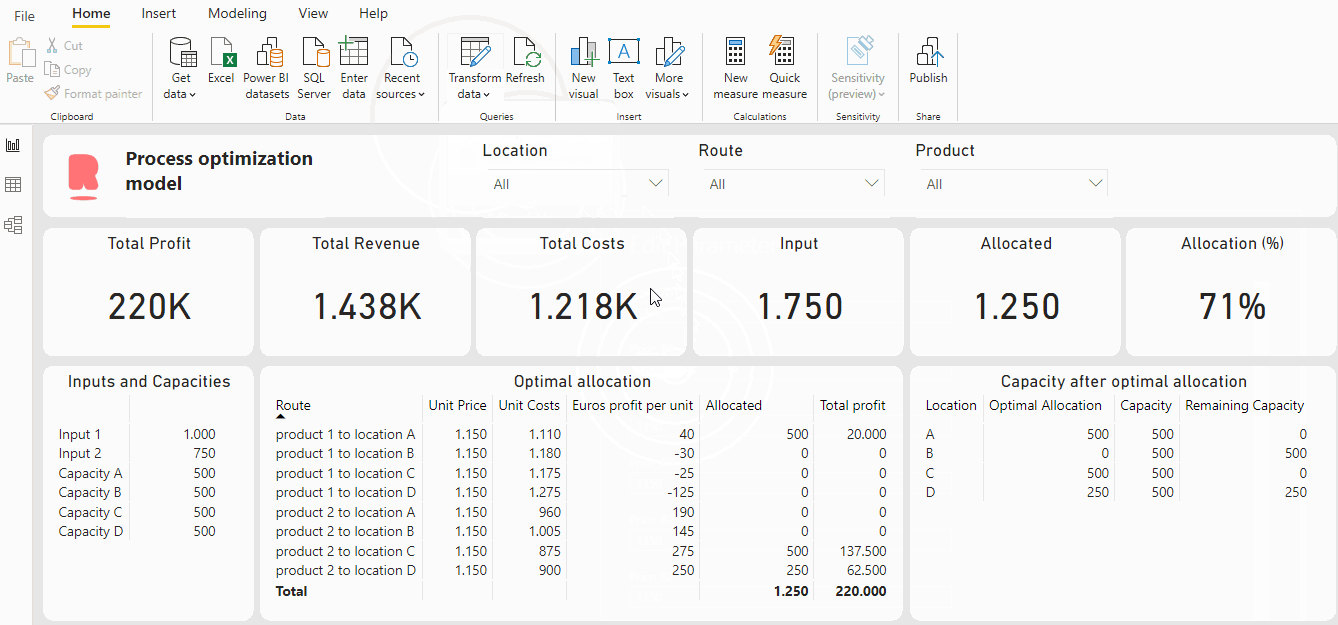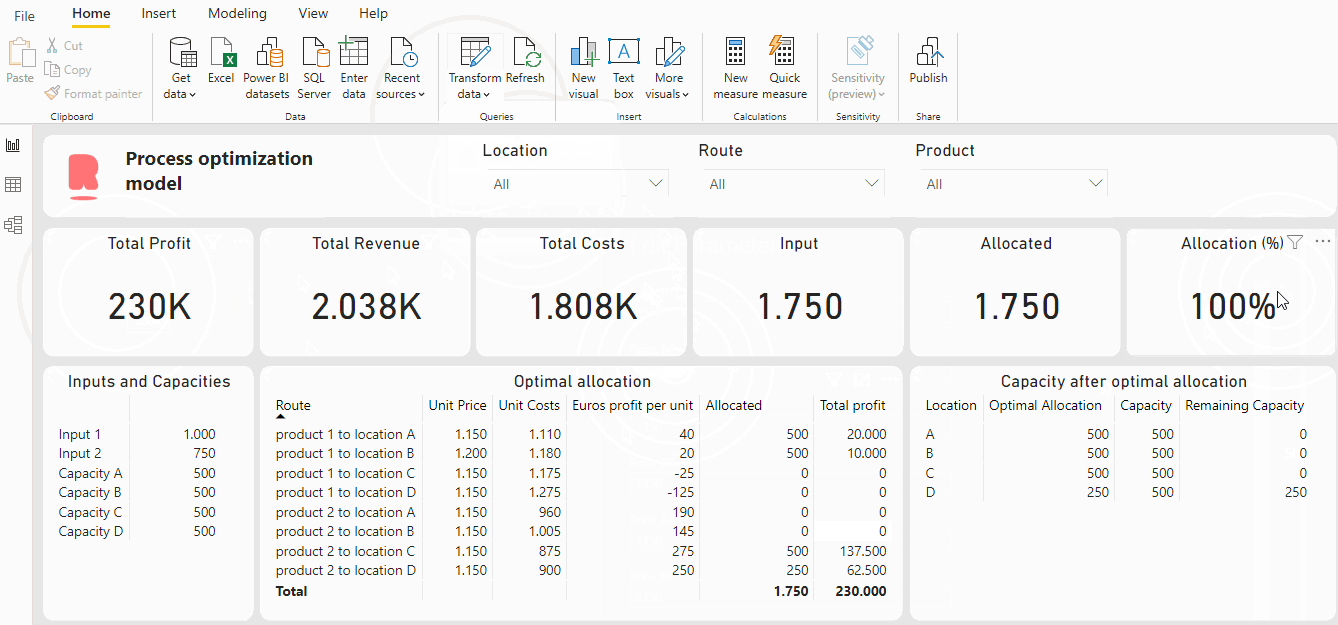
As a result of this price increase, the profit increased from 220K to 230K and all inputs are allocated. This is a quite simple example, but this can of course be extended. The possibilities are limitless!
The method used above is Linear programming or linear optimization. This is a subfield of mathematical optimization and the most common to solve process optimization problems. Linear programming is a technique to find the optimal outcome for a model where the relationship between the function and the constraint is linear.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a process optimization model helps a lot of companies to optimize their (production) process. In this blog, you learn about the possibilities of Python integrated into Power BI. Overall, a big advantage is that the end-user doesn’t need to code anything. While they can simply modify parameters and the python code will run in the background and calculate the new optimal allocation of the resources given the new variables.
Curious how process optimization can help you optimize your processes? Or are you curious how data science could help your organization with other business problems? Fill in the contact form below for a free data science discovery session!
FREE: Data Science Discovery Session
Are you curious about how process optimization can help you optimize your processes? Or how other business problems can be tackled by making use of data science? During this free discovery session, we will take a look at your business' most potential use cases.
Artificial Intelligence is ready!
In this interview, Jonathan Aardema talks with Prof. Eric Postma (professor of Cognitive Science and Artificial Intelligence at the University of Tilburg) about the why, how, and what of artificial intelligence applications. What do we see in practice, and what does science say about it?

Visiting London for the Tableau Partner Executive Kick-Off 2020
Every year Tableau invites its most valuable partners to kick off the new year together. The theme for this year was Accelerate, so let’s get right to the point. This exciting event was focused on three main areas.

Mastering DAX
Keeping your skills up to date is crucial when you work with the newest technology. At Rockfeather, we challenge each other to be the best version of yourself. That’s why I attended the mastering DAX course. DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) is a formula expression language. Next to Power BI, DAX is applied in Excel Power Pivot and tabular models in SQL Server. Learn it once, use it tomorrow.